|
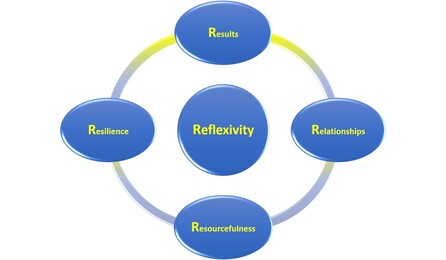
People sometimes ask if I have a guiding framework for fields of practice that range from individual and team coaching to organisation development. To be honest, it’s difficult to pin down definitively without becoming simplistic. After all, we work with people, cultures, systems and contexts that are dynamically complex. Different people, situations and times call for different interventions. Here-and-now presence, openness, curiosity and trust are prerequisite conditions for successful outcomes. That said, I often hold 5 x Rs in mind as potential areas for attention. Each R represents a different and inter-related dimension of experience, awareness and practice that commonly influences a client’s inspiration and effectiveness. The Rs are: Results, Relationships, Resourcefulness, Resilience and Reflexivity (sometimes known as ‘critical reflective practice’ or ‘praxis’). I may explore and apply these dimensions with a client at different levels ranging from intra/inter-personal to organisational. Results focuses on who or what is most important to a client and other key stakeholders and taps into e.g. vision, values, purpose, strategy, plans and outcomes. Relationships focuses on the quality of client contact with and between key stakeholders and taps into e.g. ethics, cultures, systems, synergies and dependencies. Resourcefulness focuses on solutions, strengths and opportunities in the client/environment and taps into e.g. spirituality, talent, creativity, innovation and networks. Resilience focuses on client health, wellbeing and sustainability and taps into e.g. motivation, engagement, patterns-trends, agility and flow. Reflexivity focuses on the client’s critical self- and situational awareness, stance and actions and taps into e.g. assumptions, constructs, influences, behaviours and decisions. I place the latter at the centre of this model because, at best, it radically questions, challenges and guides all other dimensions. It lays at the heart of transformational change. What frameworks do you use and find most useful?
113 Comments
I took part in an ‘immunity to change’ coaching psychology workshop this week. Based on work by Kegan and others, we looked at how and why personal and organisational change can be so difficult to achieve and sustain. The notion of immunity is taken from the physiological system where the immune system serves to protect and preserve. The psychological parallel could be regarded as an anxiety management system, designed to protect us from feelings of insecurity and threat.
The psychological immune system provides relief from anxiety. It enables us to function in the world, to maintain a degree of psychological health. The problem is that we can become locked in defended patterns of belief and behaviour, often out of conscious awareness, that prevent us facing fresh challenges and growing in resilience by surfacing, confronting and working through our deepest fears. It’s as if we become subject to our beliefs and assumptions, rather than choosing them. In the workshop, we worked through a 4-step process known as creating an X-ray or immunity map. Draw 4 columns on a sheet of paper. In the first column, write down the ‘one big thing’ about yourself that, if you could change and achieve it, would make a significant positive difference in your life and work. You may want to take feedback from others too. For example, what do key colleagues believe would make the biggest positive difference to your performance at work? In the second column, write down what you do (or, conversely, don’t do) that works against you fulfilling that goal. In other words, how do you actually behave in practice that’s different to the ‘one big thing’ that you want to characterise your behaviour in the future? Try to be very specific. ‘I do X’ or ‘I avoid doing Y’ rather than describing feelings or states of mind. You may want to ask others for feedback too on what they observe you doing or not doing, e.g. in the workplace. In the third column, start first by vividly imagining yourself behaving in real situations in the opposite way to how you described yourself behaving in the second column. Try focusing on those behaviours and situations that could feel most scary, threatening or dangerous. Allow yourself to really feel the feelings, to feel the deep discomfort, anxiety or pain that such behaviours and situations evoke for you. You may find this best to do with a coach who can provide appropriate support. In the fourth column, reflect and write down the core beliefs and deep assumptions you are carrying that lead to the feelings you are experiencing. These are often assumptions drawn from childhood experiences, e.g. ‘I must do everything perfectly if I am to be loved and accepted by others.’ Such assumptions are often unspoken, subconscious beliefs that guide our thinking, feeling and behaviour. Again, it can be useful to work with a coach to help you tease out such beliefs. This 4-step process is designed to surface underlying beliefs and assumptions that have such a powerful influence that they hold our current behaviours in place. They are the subconscious anchors that can hold us back from changing. By surfacing and ‘objectifying’ our beliefs, we have opportunity to weigh them up, examine and challenge their validity. How true are they? What evidence supports them? How well do they serve us? What alternatives could be more realistic and releasing? We closed this activity by setting up four chairs in the room, each representing one stage of the process. The person acting as ‘client’ would sit in one seat at a time while the coach coached them through that stage of the process. On completing one stage, the client would move to the next seat. We also experimented with physicality too, inviting the client to act out their goal at the first stage and their feelings at the third stage. The impact was dynamic, vivid and visual. According to the theory underpinning this approach, change efforts fail if they address profound issues at a surface, technical or behavioural level without attending to underlying psychological dynamics too. Deeply held beliefs and assumptions act like an elastic band, pulling the person back to where they started once the pressure to change is released. If the person or group is enabled to explore their personal and wider cultural beliefs, genuine transformation becomes possible. I was leading a development seminar for leaders this week, introducing various schools of psychology and their application to coaching thinking and practice, when a colleague challenged me. ‘How does Christian spirituality fit with the models you are presenting?’ It was a great question. How to develop an effective, integrative and authentic coaching approach that is consistent with Christian beliefs and values and, at the same time, draws on the best of psychological theory and coaching practice. Let me call this ‘pastoral coaching’.
The reflective practice model I’ve developed in coaching over the years could be depicted as three interlocking circles: (a) theology and spirituality, (b) theory and research, (c) experience and practice. The coach enables the client to explore and respond to these domains. The theological dimension could be conceived of as what the client and others believe about God and, thereby, as an existential metaphysic, what he, she or they believe about everything else. Spirituality could be conceived as living out personal and shared beliefs. The theory dimension is concerned with principles or conclusions drawn from experimentation, observation and critical reflection in relevant fields of thinking and practice. Research is concerned with on-going exploration, experimentation, analysis and learning. Experience is what happens when the client acts in the world. This could be conceived of in phenomenological or rational-scientific terms. Practice is about the client enacting decisions about behaviour, action and engagement in real-life relationships and situations. I was influenced some years ago by Foskett & Lyall (Helping the Helpers, 1988) who wrote an excellent book on developing supervision in the pastoral care arena. Foskett was a psychotherapist, Lyall, a university lecturer in practical theology. They proposed that Christian development tends to deal with issues from one of two perspectives: ‘applied theology’ which entails application of Biblical principles to practice or 'theological reflection’ which entails critical reflection on Biblical material in light of experience. Green in Let's do Theology (1990) illustrates the former as the ‘Swedish Method’ of engaging with biblical material. It entails posing a number of questions, e.g. what things in the passage illuminate or inspire you; what things don’t you understand; what things in the passage surprise you; what things to you agree with and approve of; what are you turned off by, reject or question; can you name something like it from elsewhere in the Bible; can you name something like it from your own life and experience; what are you now prompted to do? In contrast, Lyall in 'Pastoral Action and Theological Reflection' (Spiritual Dimensions of Pastoral Care, 2000) illustrates the latter approach through a case study. In effect, he proposes starting with a real-life experience and posing questions to it, e.g. what are the components of the situation; who is involved; what policies or protocols applied; what ethical issues did it raise; how did the past influence the present; what did decisions taken reveal about wider social or systemic values and decisions; where were the signs of God’s grace? The first approach starts with God and works out towards reflection and application; the second starts out with experience and works out towards reflection and God. Green’s book expands the theological reflection method by drawing on Kolb’s learning cycle (1984) which combines experience, perception and reflection and cognition and behaviour, and applies it to pastoral contexts. In a later text, Graham, Walton & Ward published a new book (Theological Reflection, 2005) that explored a range of theological reflection methods including theology-in-action or praxis which insists that ‘proper theological reflection cannot be formed independently of practical engagement.’ It’s this praxis model that I find most compelling. Much of the Bible itself depicts God engaging actively with people and communities in the midst of the clarity, confusion, joy and struggle of normal life. If theology as an enterprise is about knowing God and not simply knowing about him, it’s difficult to see how it can be properly developed in the abstract or in an isolated classroom environment. The challenge is how to understand and relate to God authentically without superimposing our own assumptions onto him. This is where the coaching task and agenda become significant. How to enable a person or team to make sense of complex, ambiguous experience in order to act with personal and professional integrity and to influence positive change. This is particularly important for leaders of organisations operating in fast-moving fluid environments. It’s easy to feel confused or paralysed, to lose one’s nerve, to feel draw into regressive behaviours or to sacrifice integrity for short-term expediency. Holistic coaching can play a role in helping leaders navigate turbulence and stay well. So how does this work in practice? I may start with inviting a Christian client to share an issue. It could be an issue from the Bible or an issue from experience. I may pose questions for reflection, e.g. of all the issues we could have spoken about, what is it about this issue that feels pressing or significant for you at the moment (i.e. why this, why now); how are you feeling now as you talk about it; what would you like to move towards as a result of this conversation; what questions or issues is it raising for you; what role would you like me to play? As the conversation progresses, I may pose more questions, moving around the theology and spirituality, theory and research and experience and practice model as a conceptual backdrop. Weeson in his article, Theological Reflection on Practice (The Foundations of Pastoral Studies & Practical Theology, 1986) offers a number of particularly helpful pointers for the theology and spirituality dimension that draw on his experience or mentoring students. Since this dimension is the main focus of this blog, I will quote him fully here: "Where is God's activity to be found in the situation we are exploring? Is the client's understanding of God limited so that he or she looks for His activity only in the (say) institutional framework or charismatic (personal) experience? What characteristics of God dominate the client's thinking? Can the client relate events and encounters with people to a theology of creation, providence or redemption? Does the client show theological imagination in forging an understanding of God's activity that is both true to Christian beliefs and relevant to the context? Is there a link between the experience encountered and some biblical character or situation? Can the client make connection with (say) a relevant issue which is addressed in a New Testament epistle or with the experiences of an Old Testament or a Gospel character? Are such links drawn with integrity and with due hermeneutic rigour or has the client a speculative tendency to make the Bible fit? How do proper connections throw light on an appropriate Christian strategy for engagement? How is a particularly painful or baffling situation handled? Can the client face and deal with ambiguity and complexity? Is there an ability to work with a doctrine of God or an understanding of humanity that will make some sense of the complexity? Or does the client show a tendency to run back into tidy formulations? Can the client ultimately retain convictions and yet live with areas of uncertainty? Can he or she handle this ambiguity in an encounter with a baffled person? How has an event or encounter affected the level or pattern of the client's prayer life? Has the client learned how to incorporate an ambiguous situation into his or her intercession? Has an experience resulted in a deeper meditative understanding of God and His purposes? Has the context promoted some new biblical insights which have fed personal devotion? What theological material demands further study as a result of the reflection on practice? Is there now an area (e.g. life and death, sin and salvation, justice and forgiveness, grace and truth, personal and corporate, freedom and responsibility, suffering and hope, holiness and incarnation, humility and leadership, discipline and love) where more work should be done? Has the client identified books, materials or people to help that further study?" The challenge for the coach is how to help the client or client group develop and move forward without projecting the coach’s own theological and spiritual constructs onto the client or the client’s situation. This demands high levels of self-awareness, sensitivity, wisdom, discernment and skill. The coach needs to pay close attention to his or her own intuition (‘inner voice’), the voice of the client, the indirect voice of the client’s world or system through the client and, ultimately, the voice of God. |
Nick WrightI'm a psychological coach, trainer and OD consultant. Curious to discover how can I help you? Get in touch! Like what you read? Simply enter your email address below to receive regular blog updates!
|



 RSS Feed
RSS Feed