|
‘The question is to provoke fresh thought, not to elicit an answer.’ (Stephen Guy) I thought that was a great way of framing it. At an Action Learning Facilitators’ Training event with the NHS this week, we were looking at open coaching-type questions in the exploration phase of an Action Learning round and how they differ from, say, simple questions for clarification. A great question for exploration often stops a presenter in their thinking tracks. We may notice them fall silent; gaze upwards as if on search mode; get stuck for words; speak tentatively or more…slowly. That’s very different to a presenter who answers quickly, fluently or easily – as if telling us something they already know or have already thought through for themselves. In a different Action Learning set recently, one presenter did just that. They were speaking as an expert, not as a learner, so I invited them to count to 10 silently before responding to any question posed – and invited the rest of the group to count to 10 silently too, after the presenter had spoken, before offering a next question. The idea here was to allow the questions to sink deep. Thomas Aquinas, a philosopher and theologian, commented (my paraphrase) that a great question sets us off on a journey of discovery. Brian Watts observed, similarly, that the word question itself has the word quest embedded in it. Sonja Antell invites a presenter simply – but not always easily – to ‘sit with the question’, to reflect in silence and allow the question to do its work. It’s often the place where transformation occurs.
8 Comments
'The first Advent was the embodiment of God's peace plan.' (CMEP) Advent is the anticipation of an arrival. Not just any arrival, but a re-living of the first arrival of Jesus Christ in this world. It’s also a looking forward in anticipation to the re-arrival of this Jesus in the future. In this sense, Christmas, for Christians, represents a fundamental pivotal event, a radical Kairos moment in human history. Against that backdrop, a Nigerian visitor commented in astonishment at how, in the UK, the Christmas miracle appears to have been drained of all life, vitality and meaning. We seem to have exchanged this amazing earth-shattering event for superficial, glittery materialism. Some Iranian friends asked me to explain what Christmas does mean for Christians. What’s its significance for us now? I drew on Francis Spufford’s words in Unapologetic (2012) that, if we look honestly at our own lives and across the world today, we can see evidence of the ‘human propensity to f*** things up’ everywhere. In biblical language, that’s the impact of sin (an unpopular word and concept today!). In essence, Jesus came to save us from it, to reconcile us to God and, that way, to transform humanity. We can see the effects of authentic spiritual transformation in people’s lives: ‘Mine was a happy family. I had one brother and one sister, but I do not like to talk about it. It is not important now. The important thing is to follow God’s way, the way he leads us to do something beautiful for him.’ (Mother Teresa) ‘Like anybody, I would like to live a long life. Longevity has its place. But I'm not concerned about that now. I just want to do God's will. He's allowed me to go up to the mountain top. And I've looked over. And I've seen the Promised Land.’ (Martin Luther King) ‘I have lost everything. Now I just want to know Christ, to become like him’. (Paul in Philippians, the Bible) For me, Advent is a period of critical reflection on my own faith and stance in the world, to consider how far I’m allowing God to arrive in and transform my life. As we approach the New Year, I think of Advent as preparation to venture out on a new advent-ure in faith, to discover God afresh who arrives there before us. ‘I’m not saying that I have this all together, but I am well on my way, reaching out for Jesus who has so wondrously reached out for me. I’ve got my eye on the goal where God is beckoning us onward – to Jesus. I’m running and I’m not turning back.’ (Paul in Philippians, the Bible) What does Advent mean to you? May God give you peace and hope. [See also: Arrival; Advent; Discovering our true selves] What marks out professionals from practitioners, the best from the good? It’s a great question. One thing I would suggest is critical reflective practice (CRP). It’s a semi-structured way of learning in and through experience, often with support and challenge from peers, a coach or a non-managerial supervisor. It takes willingness and commitment, an on-going desire to learn, develop and improve. I want to suggest a four-stage CRP process (based on Kolb): experience; reflect; make sense; decide.
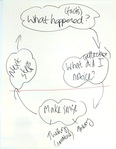
It will call us to pause, reflect and act; to be curious and test our assumptions, to expose our sometimes uncomfortable feelings and – for me – to pray for discernment and wisdom. Here are some sample questions. Firstly, experience: What happened? What was/am I aware of? Where was/is my attention? What was/am I feeling? What was/is the impact? Secondly, reflect: What was my intention? What beliefs or values were at play? What didn’t I notice? What assumptions was/am I making? What other options were/are available? Thirdly, make sense: What are the bigger-picture issues (e.g. politics/principles)? What wider team or organisational issues does it reveal? What is the generic issue (e.g. conflict)? What theory or research could I draw on to inform my thinking and practice? What hypotheses am I making? Finally, decide: What have I learned through this? What do I need to do the same or differently in future? How I will I prepare next time? Do any wider issues need to be addressed? What will my next step be? The third stage, ‘make sense’ distinguishes critical reflective practice from simple reflection on practice. It draws the experience and learning of others including academics and peers into the frame. It’s also the area that many professionals neglect because of time constraints – or because they are not sure how to do it. Simple ideas: journals, books, networks, conferences and LinkedIn groups. How good are you at critical reflective practice? What do you do to develop and sustain it? I met with a group of leaders last week whose roles include mentoring, supervision and pastoral support. The focus of our time together was how to learn and use a coaching approach to enhance the work they do with people and groups. In the midst of conversation, some said they would be interested to hear more about reflective practice and how to do it using coaching skills. Time was short so I hastily scribbled a reflective practice cycle on a flipchart. It draws on work by Argyris, Schon and Honey & Mumford. I explained that there are at least two ways we can think about this. Classical educationalists often start from a focus on theory, core principles etc. (and, in this group’s case, theology) and then move on to look at how to apply the theory to practice. By contrast, reflective practice often starts from observation of an experience (or experiment), then moves on to reflection on that experience, then to consider how it resonates with, challenges or informs a hypothesis or theory. This implies critical thinking and by extension, aims to guide future practice. In this sense, it shares common principles with related fields such as action research. And so how to apply a coaching approach… 1. Contracting: What are we here to do? How shall we do this? 2. Observation: What happened? What were you aware of? 3. Awareness: How did you feel? What assumptions were you making? 4. Sense-making: What surprised or confused you? How does it fit (or not) with what you know/believe? 5. Learning: ‘What have you discovered in this? 6. Action: And so..? What next? When was the last time you paid detailed attention to how you walked across a room at home to open the door? When was the last time you had one of those car journeys where, when you arrived at your destination, you couldn’t remember anything of the journey? The ability of the human body and mind to run on auto-pilot is quite amazing. It enables us to fulfil familiar tasks with minimal conscious effort and attention, thereby allowing us to focus on other things we want or need to.
That’s the upside. And it’s a very useful upside for day-to-day life and work. The downside is that, in some situations, doing what we do because that’s what we do can cause us to miss important factors, significant variables and valuable learning opportunities. This is where reflective practice comes in. It’s what is says on the proverbial tin: reflection before, during and after action. Easier said than done, you may say. True: so here are some tips from experience that I’ve found useful. Tip 1: Pause. If you don’t stop to think from time to time, you may not stop to think at all. Tip 2: Plan. Choose key moments for critical reflection, e.g. at the start of a project – ‘What are we here to do?’; mid-way through – ‘How are we doing?’; afterwards – ‘What are we learning?’ Tip 3: Provoke. Seek out stimulating literature; work with contrasting cultures; invite people to test your assumptions. Tip 4: Practise. Reflective practice takes…erm…practice. Pause, reflect act. Act pause reflect. We often think of coaching as creating a special space for a person to step back, often quite literally, from the pressures of day to day work and life to think about things differently. Indeed, the space we create between coach and coachee offers a great opportunity for change.
Yet space is a bit like elastic. Too much space and coaching can feel slack and lifeless, without definition or form. Too much pace and it can feel rushed, superficial and forced. Navigating space and pace is part of the, ‘How shall we do this?’ contract between coach and coachee. The same question arises in leadership, training and facilitation. When to up the tempo, inject energy, move quickly. When to pause, breathe, process. It’s tricky in mixed groups. Activists want to get on with it. Suck it and see. Reflectors want space to observe it. Make sense of it. So I try to remember: just enough space to allow for reflection; just enough pace to keep things moving. It’s always a judgement call. How much space and pace does this person or group need - in this situation, at this time? If in doubt, discuss it openly and ask for feedback. When teams are under pressure, e.g. dealing with critical issues, sensitive topics or working to tight deadlines, tensions can emerge that lead to conversations getting stuck. Stuck-ness between two or more people most commonly occurs when at least one party’s underlying needs are not being met, or a goal that is important to them feels blocked.
The most obvious signs or stuck-ness are conversations that feel deadlocked, ping-pong back and forth without making progress or go round and round in circles. Both parties may state and restate their views or positions, wishing the other would really hear. If unresolved, responses may include anger/frustration (fight) or disengagement/withdrawal (flight). If such situations occur, a simple four step process can make a positive difference, releasing the stuck-ness to move things forward. It can feel hard to do in practice, however, if caught up in the drama and the tense feelings that ensue! I’ve found that jotting down questions as an aide memoire can help, especially if stuck-ness is a repeating pattern. 1. Observation. (‘What’s going on?’). This stage involves metaphorically (or literally) stepping back from the interaction to notice and comment non-judgementally on what’s happening. E.g. ‘We’re both stating our positions but seem a bit stuck’. ‘We seem to be talking at cross purposes.’ 2. Awareness. (‘What’s going on for me?’). This stage involves tuning into my own experience, owning and articulating it, without projecting onto the other person. E.g. ‘I feel frustrated’. ‘I’m starting to feel defensive.’ ‘I’m struggling to understand where you are coming from.’ ‘I’m feeling unheard.’ 3. Inquiry. (‘What’s going on for you?’). This stage involves inquiring of the other person in an open spirit, with a genuine, empathetic, desire to hear. E.g. ‘How are you feeling?’ ‘What are you wanting that you are not receiving?’ ‘What’s important to you in this?’ ‘What do you want me to hear?’ 4. Action. ('What will move us forward?’) This stage involves making requests or suggestions that will help move the conversation forward together. E.g. ‘This is where I would like to get to…’ ‘It would help me if you would be willing to…’. ‘What do you need from me?’ ‘How about if we try…’ Shifting the focus of a conversation from content to dynamics in this way can create opportunity to surface different felt priorities, perspectives or experiences that otherwise remain hidden. It can allow a breathing space, an opportunity to re-establish contact with each other. It can build understanding, develop trust and accelerate the process of achieving results. How would you describe your coaching style? What questions would you bring to a client situation?
In my experience, it depends on a whole range of factors including the client, the relationship, the situation and what beliefs and expertise I, as coach, may hold. It also depends on what frame of reference or approach I and the client believe could be most beneficial. Some coaches are committed to a specific theory, philosophy or approach. Others are more fluid or eclectic. Take, for instance, a leader in a Christian organisation struggling with issues in her team. The coach could help the leader explore and address the situation drawing on any number of perspectives or methods. Although not mutually exclusive, each has its own focus and emphasis. The content and boundaries will reflect what the client and coach believe may be significant: Appreciative/solutions-focused: e.g. ‘What would an ideal team look and feel like for you?’, ‘When has this team been at its best?’, ‘What made the greatest positive difference at the time?’, ‘What opportunity does this situation represent?’, ‘On a scale of 1-10, how well is this team meeting your and other team members’ expectations?’, ‘What would it take to move it up a notch?’ Psychodynamic/cognitive-behavioural: e.g. ‘What picture comes to mind when you imagine the team?’, ‘What might a detached observer notice about the team?’, ‘How does this struggle feel for you?’, ‘When have you felt like that in the past?’, ‘What do you do when you feel that way?’, ‘What could your own behaviour be evoking in the team?’, ‘What could you do differently?’ Gestalt/systemic: e.g. ‘What is holding your attention in this situation?’ ‘What are you not noticing?’, ‘What are you inferring from people’s behaviour in the team?’, ‘What underlying needs are team members trying to fulfil by behaving this way?’, ‘What is this team situation telling you about wider issues in the organization?’, ‘What resources could you draw on to support you?’ Spiritual/existential: e.g. ‘How is this situation affecting your sense of calling as a leader?’, ‘What has God taught you in the past that could help you deal with this situation?’, ‘What resonances do you see between your leadership struggle and that experienced by people in the Bible?’, ‘What ways of dealing with this would feel most congruent with your beliefs and values?’ An important principle I’ve learned is to explore options and to contract with the client. ‘These are some of the ways in which we could approach this issue. What might work best for you?’ This enables the client to retain appropriate choice and control whilst, at the same time, introduces possibilities, opportunities and potential new experiences that could prove transformational. What are your favourite coaching questions? I often use 3 that I’ve found can create a remarkable shift in awareness, insight and practice, especially in team coaching. I’ve applied them using variations in language and adapted them to different client issues, opportunities and challenges. They draw on principles from psychodynamic, Gestalt and solutions-focused coaching and are particularly helpful when a client or team feels stuck, unable to find a way forward.
* ‘What’s your contribution to what you are experiencing?’ * ‘What do you need, to contribute your best?’ * ‘What would it take..?’ Client: ‘These meetings feel so boring! I always leave feeling drained rather than energised.’ Coach: ‘What’s your contribution to what you are experiencing?’ Client: ‘Excuse me?’ Coach: ‘What do you do when you feel bored?’ Client: ‘I drift away, look out of the window.’ Coach: ‘What might be the impact on the wider group when you drift away?’ Client: ‘I guess others may disengage too.’ Coach: ‘How does the meeting feel when people disengage?’ Client: 'Hmmm…boring!’ Coach: ‘What do you need to contribute your best?’ Client: ‘It would help certainly if we could negotiate and agree the agenda beforehand, rather than focus on things that feel irrelevant.’ Coach: ‘So you want to ensure the agenda feels relevant to you. What else?’ Client: ‘If we could meet off site and break for coffee from time to time, that would feel more energising.’ Coach: ‘So venue and breaks make a difference too. Anything else?’ Client: ‘No, that’s it.’ Client: ‘I don’t think I can influence where and how these meetings are held.’ Coach: ‘It sounds like you feel quite powerless. How would you rate your level of influence on a scale of 1-10?’ Client: ‘Around 3’. Coach: ‘What would it take to move it up to a 6 or 7?’ Client: ‘I guess if I showed more support in the meetings, the leader may be more open to my suggestions.’ Coach: ‘What else would it take?’ Client: ‘I could work on building my relationship with the leader outside of meetings too.’ These type of questions can help a client grow in awareness of the interplay between intrapersonal, interpersonal and group dynamics, his or her impact within a wider system, what he or she needs to perform well and how to influence the system itself. They can also shift a person or team from mental, emotional and physical passivity to active, optimistic engagement. What are your favourite coaching questions? How have you used them and what happened as a result? I took my mountain bike for repairs last week after pretty much wrecking it off road. In the same week, I was invited to lead a session on ‘use of self’ in coaching. I was struck by the contrast in what makes a cycle mechanic effective and what makes the difference in coaching. The bike technician brings knowledge and skill and mechanical tools. When I act as coach I bring knowledge and skills too - but the principal tool is my self.
Who and how I am can have a profound impact on the client. This is because the relationship between the coach and client is a dynamically complex system. My values, mood, intuition, how I behave in the moment…can all influence the relationship and the other person. It works the other way too. I meet the client as a fellow human being and we affect each other. Noticing and working with with these effects and dynamics can be revealing and developmental. One way of thinking about a coaching relationship is as a process with four phases: encounter, awareness, hypothesis and intervention. These phases aren’t completely separate in practice and don’t necessarily take place in linear order. However, it can provide a simple and useful conceptual model to work from. I’ll explain each of the four phases below, along with key questions they aim to address, and offer some sample phrases. At the encounter phase, the coach and client meet and the key question is, ‘What is the quality of contact between us?’ The coach will focus on being mentally and emotionally present to the client…really being there. He or she will pay particular attention to empathy and rapport, listening and hearing the client and, possibly, mirroring the client’s posture, gestures and language. The coach will also engage in contracting, e.g. ‘What would you like us to focus on?’, ‘What would a great outcome look and feel like for you?’, ‘How would you like us to do this?’ (If you saw the BBC Horizon documentary on placebos last week, the notion of how a coach’s behaviour can impact on the client’s development or well-being will feel familiar. In the TV programme, a doctor prescribed the same ‘medication’ to two groups of patients experiencing the same physical condition. The group he behaved towards with warmth and kindness had a higher recovery rate than the group he treated with clinical detachment). At the awareness phase, the coach pays attention to observing what he or she is experiencing whilst encountering the client. The key question is, ‘What am I noticing?’ The coach will pay special attention to e.g. what he or she sees or hears, what he or she is thinking, what pictures come to mind, what he or she is feeling. The coach may then reflect it back as a simple observation, e.g. ‘I noticed the smile on your face and how animated you looked as you described it.’ ‘As you were speaking, I had an image of carrying a heavy weight…is that how it feels for you?’ ‘I can’t feel anything...do you (or others) know how you are feeling?’ (Some schools, e.g. Gestalt or person-centred, view this type of reflecting or mirroring as one of the most important coaching interventions. It can raise awareness in the client and precipitate action or change without the coach or client needing to engage in analysis or sense-making. There are resonances in solutions-focused coaching too where practitioners comment that a person doesn’t need to understand the cause of a problem to resolve it). At the hypothesis stage, the coach seeks to understand or make sense of what is happening. The key question is, ‘What could it mean?’ The coach will reflect on his or her own experience, the client’s experience and the dynamic between them. The coach will try to discern and distinguish between his or her own ‘stuff’ and that of the client, or what may be emerging as insight into the client’s wider system (e.g. family, team or organisation). The coach may pose tentative reflections, e.g. ‘I wonder if…’, ‘This pattern could indicate…’, ‘I am feeling confused because the situation itself is confusing.’ (Some schools, e.g. psychodynamic or transactional analysis, view this type of analysis or sense-making as one of the most important coaching interventions. According to these approaches, the coach brings expert value to the relationship by offering an explanation or interpretation of what’s going on in such a way that enables the client to better understand his or he own self or situation and, thereby, ways to deal with it). At the intervention phase, the coach will decide how to act in order to help the client move forward. Although the other three phases represent interventions in their own right, this phase is about taking deliberate actions that aim to make a significant shift in e.g. the client’s insight, perspective, motivation, decisions or behaviour. The interventions could take a number of forms, e.g. silence, reflecting back, summarising, role playing or experimentation. Throughout this four-phase process, the coach may use ‘self’ in a number of different ways. In the first phase, the coach tunes empathetically into the client’s hopes and concerns, establishing relationship. In the second, the coach observes the client and notices how interacting with the client impacts on him or herself. The coach may reflect this back to the client as an intervention, or hold it as a basis for his or her own hypothesising and sense-making. In the third, the client uses learned knowledge and expertise to create understanding. In the fourth, the coach presents silence, questions or comments that precipitate movement. In schools such as Gestalt, the coach may use him or herself physically, e.g. by mirroring the client’s physical posture or movement or acting out scenarios with the client to see what emerges. In all areas of coaching practice, the self is a gift to be used well and developed continually. |
Nick WrightI'm a psychological coach, trainer and OD consultant. Curious to discover how can I help you? Get in touch! Like what you read? Simply enter your email address below to receive regular blog updates!
|





 RSS Feed
RSS Feed